Host Filters
Overview
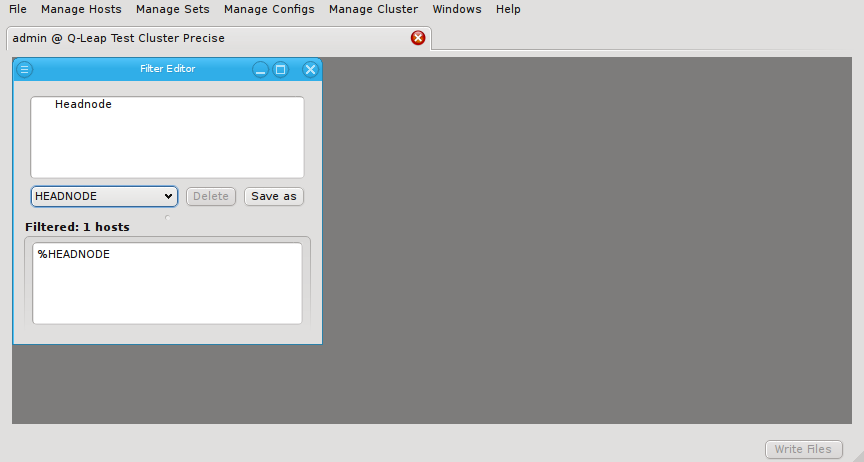
Host filters define a set of hosts by specifying any number of criteria. The set of hosts
defined by a filter is dynamic: Changes made to the properties of hosts are automatically
reflected in the hostlist a filter evaluates to. Every time a filter is used, the criteria
defining it are evaluated from scratch. Hence, host filters provide a powerful tool to classify
hosts into groups, in a way that will dynamically take into account changes made to the
cluster. They can be used in various ways within QluMan:
-
In pre-defined commands to either specify, the set of hosts, where a command should be executed or to supply the resulting hostlist as an argument to the command.
-
As user input for pre-defined or custom commands.
-
In the Enclosure View to modify the selection.
-
As a temporary filter for quickly selecting hosts to execute commands on using the Remote Execution Engine or to modify the selection in the Enclosure View.
Host Filter Editor
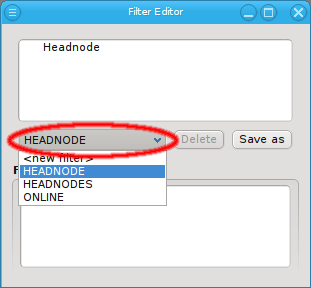
The filter editor window is split into two areas. At the top, the definition of the currently selected filter is shown. You can select the filter to be displayed from the drop-down menu. At the bottom, the hosts that currently pass all the filters are displayed in the compact hostlist format. This format is used by a number of other programs including pdsh and SLURM (the pdsh Wiki has a detailed discussion on the syntax).
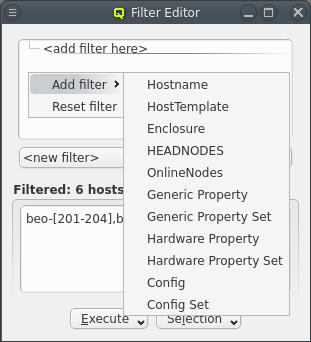
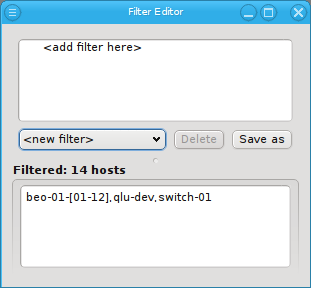
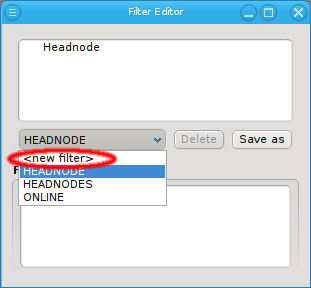
Select New filter from the drop-down menu to start defining a new filter. Then add specific sub-filters from the context menu, until the desired subset of hosts is displayed in the bottom half of the window. Using their context-menu, filters can be edited or removed and sub-filters be added.
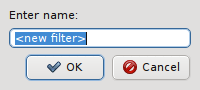
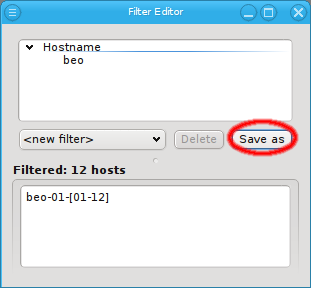
The Reset filter menu item clears the filter, so one can start from scratch. To finally create (save) the new filter click Save as and enter a name for it.
Editing a Filter
Editing a filter is similar to creating a new one. First select the filter from the drop-down menu to display it’s current definition. Then add, edit or remove individual filters as desired. Finally click Save as to save the altered filter, Using an existing name will replace the old filter. Using a different name will create a new filter.
Types of Filters

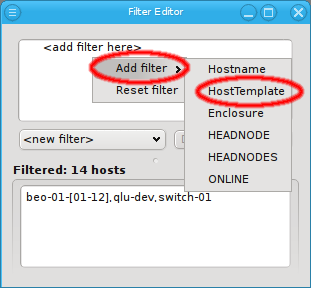
A filter can be added from the context menu (right mouse click) in the top area. For a host to
show up in the filtered list (bottom part), it must pass all the filters added. Each filter may
narrow down the list. Any number of filters can be added and they do not have to be unique. For
example you can add a Hostname filter that selects all hosts that begin with beo and a Host
Template filter that selects all Demo VM nodes. A host has to pass all top-level filters to
show up. Currently, QluMan provides six top-level filters: Hostname, HostTemplate, Enclosure,
HEADNODE, HEADNODES and ONLINE. Additional ones will be added in the future.
Hostname Filter
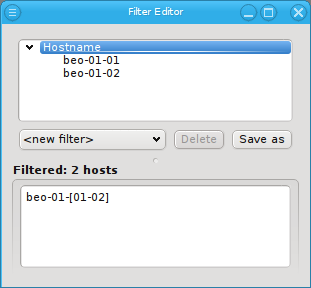
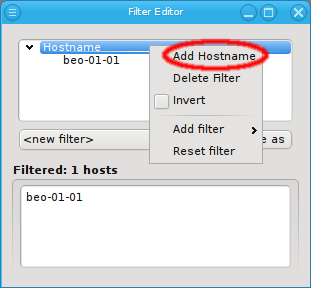
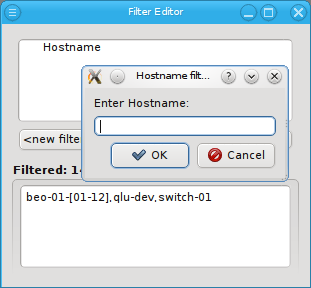
Adding a Hostname filter opens up a pop-up dialog asking for the hostname or a regular
expression to filter for. The input must be a regular expression in python syntax and is
matched against the beginning of the hostname. If a match against the full hostname is desired
then "$" should be added at the end. A ".*" can be added to the front, to match anywhere in the
hostname instead of matching against the beginning.
|
Multiple hostname patterns can be added to a Hostname filter through the context menu. This is additive: If a host matches at least one pattern, it will be included in the resulting list. |
Host Template Filter
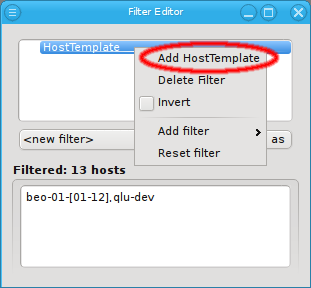
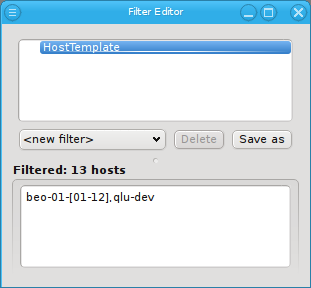
Adding a Host Template filter does not pop up a dialog. Instead it adds an empty Host Template filter. This simply selects all hosts with an assigned Host Template. Hosts that do not have a Host Template will not pass this filter. The filter can be made more specific by adding Host Template patterns to it through the context menu.
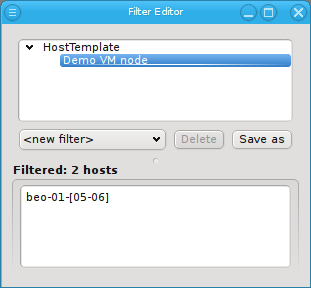
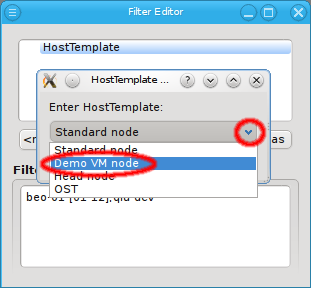
This opens up a pop-up dialog, from where an existing Host Template name can be selected. The result is a list of hosts, for which the associated Host Template matches the given pattern. Adding multiple Host Template names is again additive, just like with Hostname patterns.
Enclosure Filter
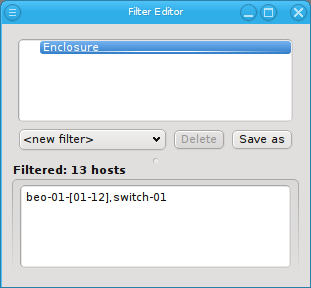
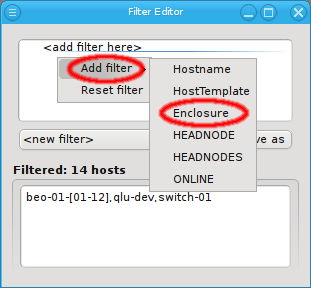
Adding an Enclosure filter does not bring up a dialog either. Like a Host Template filter, it selects all hosts that are part of an enclosure. Unlike the Hostname and Host Template filters though, an Enclosure filter allows for two different specifications: The name and/or the type of an enclosure can be matched. Just like Hostname and Host Template filters the Enclosure filter is additive.
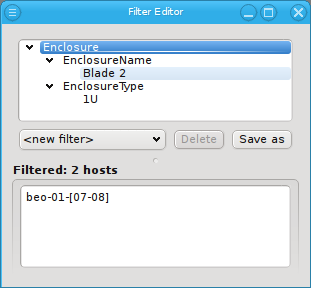
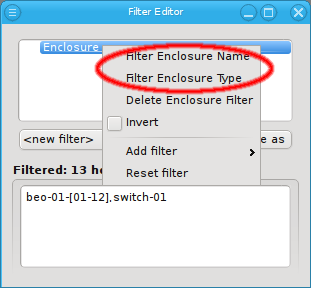
Adding sub-filters for both the Enclosure name and the Enclosure type will filter hosts that match at least one of those criteria. To filter for hosts that match both, an Enclosure name and an Enclosure type, two separate Enclosure filters have to be used to get the intersection of both filters. The first one to filter the name and the second one to filter the type.
Property/Config Set Filter
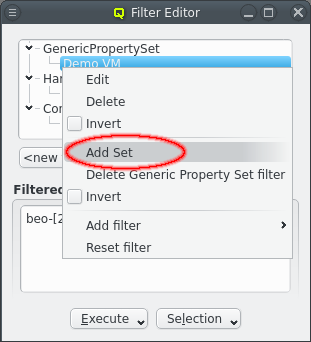
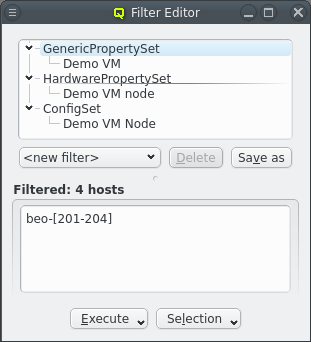
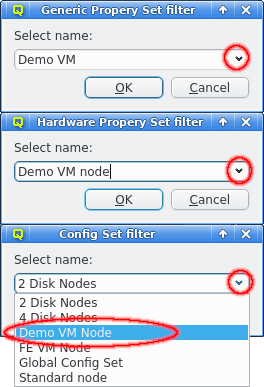
The Host Template filter selects hosts that have a very specific config. On the other hand, the Generic/Hardware Property and Config Set filters allow filtering for just one branch of the overall configuration. They also work when a set is assigned via the Global Host Template or assigned directly to a host. Adding one of these filters opens up a pop-up dialog asking for the set to filter for.
|
Only the relevant set of a host is used to evaluate the filter. This set is (in this order) either a directly assigned one, the one of an assigned Host Template or if none of these are assigned, the one of the Global Host Template. |
|
Multiple sets can be added to a Set filter via the context-menu. This is additive: If a host is assigned to any one of these sets, it will be included in the resulting list. |
Property/Config Filter
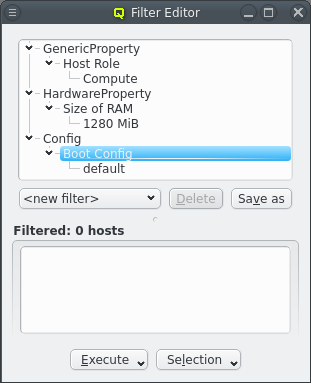
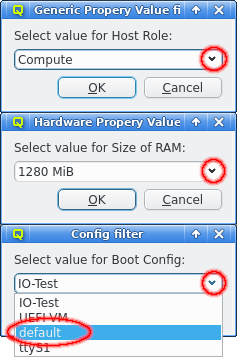
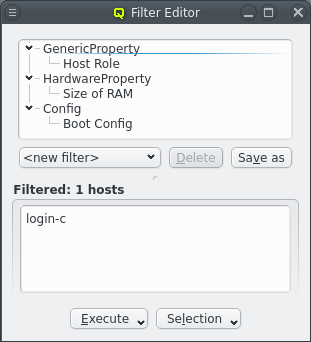
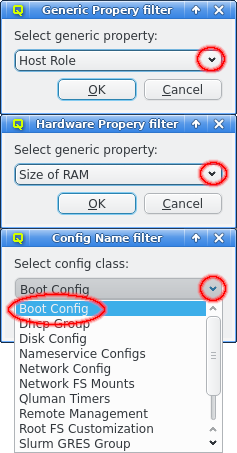
The Generic/Hardware Property and Config Filter allow filtering for even more selective configurations options. Adding one of these filters opens up a pop-up dialog asking for the type of property or config class to filter for. This will select hosts that have any value configured for the selected property or config class.
This can be further restricted to only filter for hosts that have set a specific value for the property or config class by selecting Add Value from the context menu.
|
A property or config class can be set from the Global Host Template, the Host Template, from a directly assigned set or a direct assignment. While some properties or config classes allow assigning multiple values, only the value(s) assigned from the relevant level take effect and are used for the filter. |
|
Multiple values can be added to a Generic/Hardware Property or Config filter through the context-menu. This is additive: If a host has set any one of these values, it will be included in the resulting list. |
Inverting a Filter
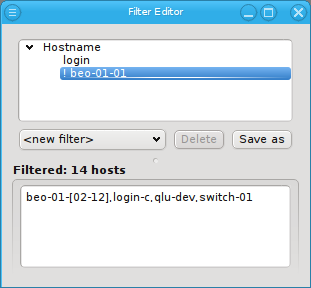
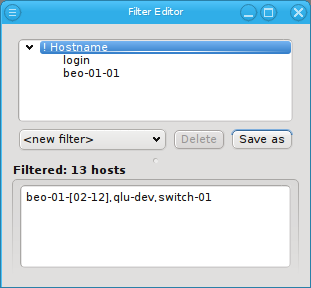
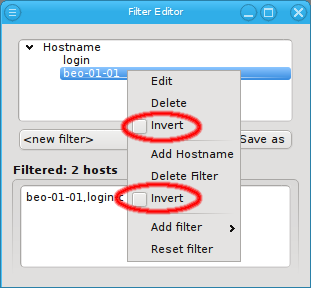
Every filter, sub-filter and pattern can be inverted through the context menu. The context menu for a pattern contains menu entries for both, the pattern and the enclosing filter separated by a line. The first Invert entry will invert the specific pattern that was selected, while the second Invert will invert the whole filter.
Besides the obvious, this can also be useful in finding hosts that are not configured correctly. For example, adding an empty Host Template filter and inverting it, will show all hosts without a Host Template. Adding a second filter, that selects all switches, power controllers and other special devices (they usually don’t need a Host Template) and also inverting that, results in a list of all hosts, that are neither properly configured nodes (missing Host Template) nor special devices.
Additive versus subtractive
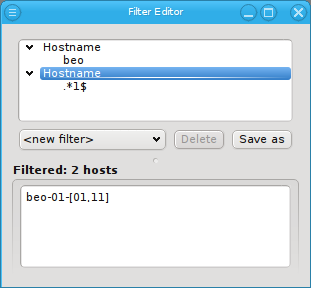
When constructing a filter, it is important to remember, that all top-level filters are
subtractive. A host must pass all top-level filters to show up in the result. On the other
hand, all patterns and sub-filters are additive. Matching any one of them within a top-level
filter adds the host to the result of that filter. Hence, when subtractive behavior is desired
for patterns or sub-filters, each pattern or sub-filter must be added to its own top-level
filter. For example, to select all hosts that start with beo as well as end on "1", two
Hostname filters have to be added.
Using temporary Filters
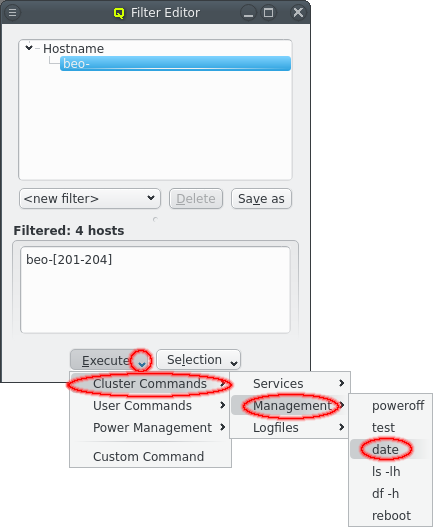
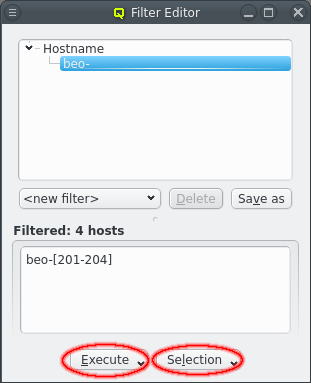
A filter remains temporary unless it is saved. But it can already be used directly from the Filter Editor using the Execute or Selection buttons.
The Execute button is a shortcut to the Remote Execution Engine and will use the current filter results to fill in the Execute on part of the selected command.
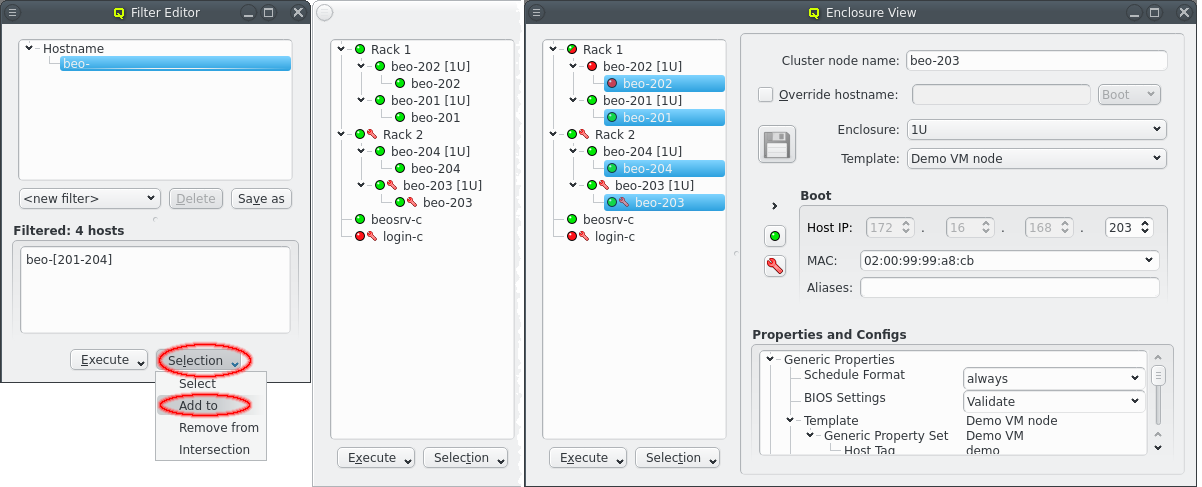
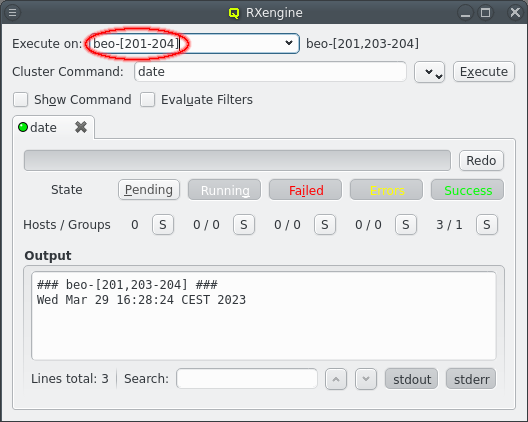
The Selection button allows modifying the selection of hosts in the Enclosure View. The selection can be set to the filter result itself, the filtered hosts can be added to or removed from an existing selection or the intersection of the filtered hosts and the current selection can be constructed.